In a world where pharmaceuticals play a vital role in healthcare, ensuring the safety of medications remains a paramount concern. Pharmacovigilance, the science of monitoring and assessing the safety of medical products, takes center stage in this endeavor. However, the scope of pharmacovigilance goes beyond individual countries; it reaches across borders to create a comprehensive global safety net.
Pharmacovigilance regulations are the backbone of medication safety. They lay down the guidelines and procedures for monitoring adverse reactions, assessing risks, and taking necessary actions to ensure that the benefits of medications far outweigh their potential risks. By enforcing these regulations, regulatory bodies around the world guarantee that every medication entering the market is subjected to rigorous scrutiny, contributing to public health protection.
The interconnected nature of today’s pharmaceutical landscape underscores the necessity of global collaboration in pharmacovigilance. As medications are produced, distributed, and consumed on a worldwide scale, a unified approach becomes paramount. Global collaboration harmonizes practices, enabling regulatory agencies, healthcare professionals, and pharmaceutical companies from various countries to exchange information, share best practices, and collectively address safety concerns.
In this blog post, we embark on a journey through the intricate web of pharmacovigilance regulations and the invaluable role of global collaboration. We will explore how different nations come together, align their efforts, and foster a collective commitment to ensuring medication safety. As we delve deeper into this topic, we will uncover the challenges, opportunities, and real-world impact of this collaborative approach. Join us to discover how the collective commitment to pharmacovigilance transcends boundaries for the well-being of patients worldwide.
Connected posts of topic, if missed
Must read
Table of Contents
Regulatory Frameworks
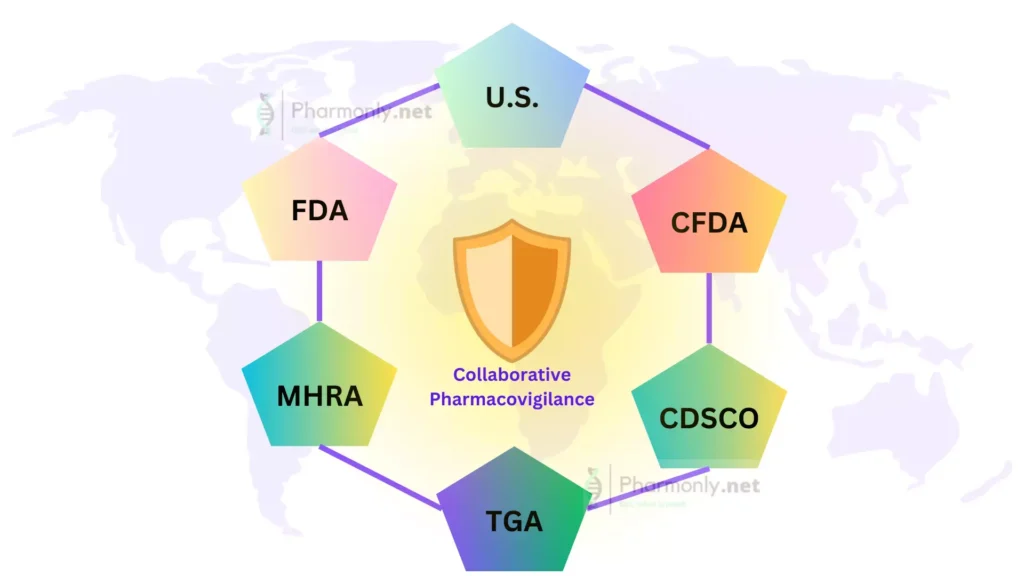
Pharmacovigilance regulations find their foundation in a network of regulatory agencies and bodies that oversee the safety of medications. These entities are entrusted with the critical task of ensuring that the drugs available in the market are safe and effective for public consumption. Let’s delve into some key pharmacovigilance regulatory agencies and understand their roles in shaping drug safety practices globally.

FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration)
The FDA stands as a prominent guardian of drug safety. Responsible for regulating drugs and medical devices in the United States, the FDA meticulously evaluates drug applications and monitors post-market safety data. Through its MedWatch program, the FDA encourages healthcare professionals and patients to report adverse events, playing a pivotal role in identifying emerging safety concerns.
EMA (European Medicines Agency)
The EMA operates as the central hub for drug evaluation within the European Union. It evaluates and supervises medicinal products, and its Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) assesses safety issues. The EMA actively collaborates with other regulatory agencies globally to share safety data, ensuring a harmonized approach to drug safety across borders.
WHO (World Health Organization)
On the international stage, the WHO plays a crucial role in coordinating pharmacovigilance efforts. Its Programme for International Drug Monitoring (PIDM) facilitates communication among national pharmacovigilance centers, promoting information exchange and collaborative signal detection. The WHO’s global perspective ensures that even less-resourced countries have access to critical drug safety information.
Roles and Responsibilities
These regulatory agencies share common objectives in monitoring drug safety, but their roles and responsibilities may differ based on regional nuances. They evaluate drug applications before approval, continuously assess post-market safety data, and issue guidelines for pharmacovigilance practices. These guidelines empower pharmaceutical companies and healthcare professionals to report adverse events promptly, ensuring early detection and appropriate actions.
In essence, the collaborative efforts of these agencies set the stage for a standardized approach to pharmacovigilance worldwide. By meticulously reviewing safety data, issuing guidelines, and fostering global partnerships, they collectively uphold the safety of medications, safeguarding public health on a global scale. In the next sections, we’ll delve into the pharmacovigilance regulations adopted by various countries and explore the impact of these regulatory frameworks on drug safety practices.
Pharmacovigilance Regulations in Different Countries
As the pharmaceutical landscape transcends borders, pharmacovigilance regulations vary across countries while collectively aiming to ensure the safety of medications. Let’s embark on a journey around the world to understand the diverse approaches taken by different nations, as well as the common threads that weave them together.
USA: Rigorous Reporting and Vigilance
In the United States, the FDA’s pharmacovigilance framework emphasizes thorough reporting. Pharmaceutical companies are mandated to submit adverse event reports, and healthcare professionals and patients are encouraged to participate through the FDA’s MedWatch program. The FDA continuously evaluates data to detect signals, assess risks, and take timely actions to protect public health.
EU Member States: Collaborative Vigilance
The European Union operates under a decentralized system where each member state contributes to pharmacovigilance efforts. The EMA coordinates their collective actions and sets guidelines to harmonize practices. The Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) conducts safety assessments, fostering a collaborative approach to signal detection and risk assessment.
Japan: Stringent Monitoring
Japan’s Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) oversees pharmacovigilance within the country. Rigorous monitoring and assessment are integral to Japan’s approach, with a strong emphasis on post-market surveillance. Reporting adverse events and conducting risk assessments are essential components of Japan’s pharmacovigilance strategy.
Canada: Proactive Monitoring
In Canada, the Canada Vigilance Program plays a pivotal role in pharmacovigilance. Reporting adverse events is mandatory for healthcare professionals, and voluntary reporting is encouraged from patients and consumers. The program actively engages in signal detection and assessment to identify emerging safety concerns.
Variations and Common Threads
While each country’s pharmacovigilance regulations have unique nuances, common threads weave them together. Reporting requirements are a universal theme, encouraging healthcare professionals, patients, and pharmaceutical companies to contribute to the safety database. Signal detection and risk assessment form the backbone of drug safety practices globally, regardless of regional differences.
Harmonizing for Global Impact
The variations in pharmacovigilance regulations reflect the diverse healthcare landscapes and priorities of different countries. However, the shared commitment to ensuring medication safety unites them. As these countries collaborate through international networks and information sharing, their collective efforts contribute to a safer healthcare environment for people around the world.
In the upcoming sections, we’ll delve into the challenges and opportunities that arise from this global diversity in pharmacovigilance regulations. We’ll explore how these regulations intersect to create a harmonized approach to safeguarding public health while respecting individual national contexts.
Good Pharmacovigilance Practice: Guidelines for Pharmacovigilance
Good Pharmacovigilance Practice (GVP) refers to a set of guidelines and practices aimed at ensuring the safety, efficacy, and quality of medicinal products by systematically monitoring and managing their risks throughout their lifecycle. GVP guidelines are established by various regulatory authorities and international organizations to provide a framework for pharmacovigilance activities. GVP encompasses a wide range of activities, including adverse event reporting, signal detection, risk management, and safety communication. Here are the key components of good pharmacovigilance practice:
- Introduction to Pharmacovigilance: Pharmacovigilance involves monitoring, assessing, and preventing adverse effects of drugs after they’re on the market. It’s essential for patient safety and maintaining public trust in medications.
- Pharmacovigilance Systems: Effective systems ensure proper data collection, assessment, and reporting of adverse events. Stakeholders like regulators, manufacturers, and healthcare professionals have defined roles, and standardized procedures are essential.
- Adverse Event Reporting: Timely collection and reporting of adverse events, categorized by severity, are critical. Regulatory guidelines specify reporting criteria and deadlines to ensure accurate safety information.
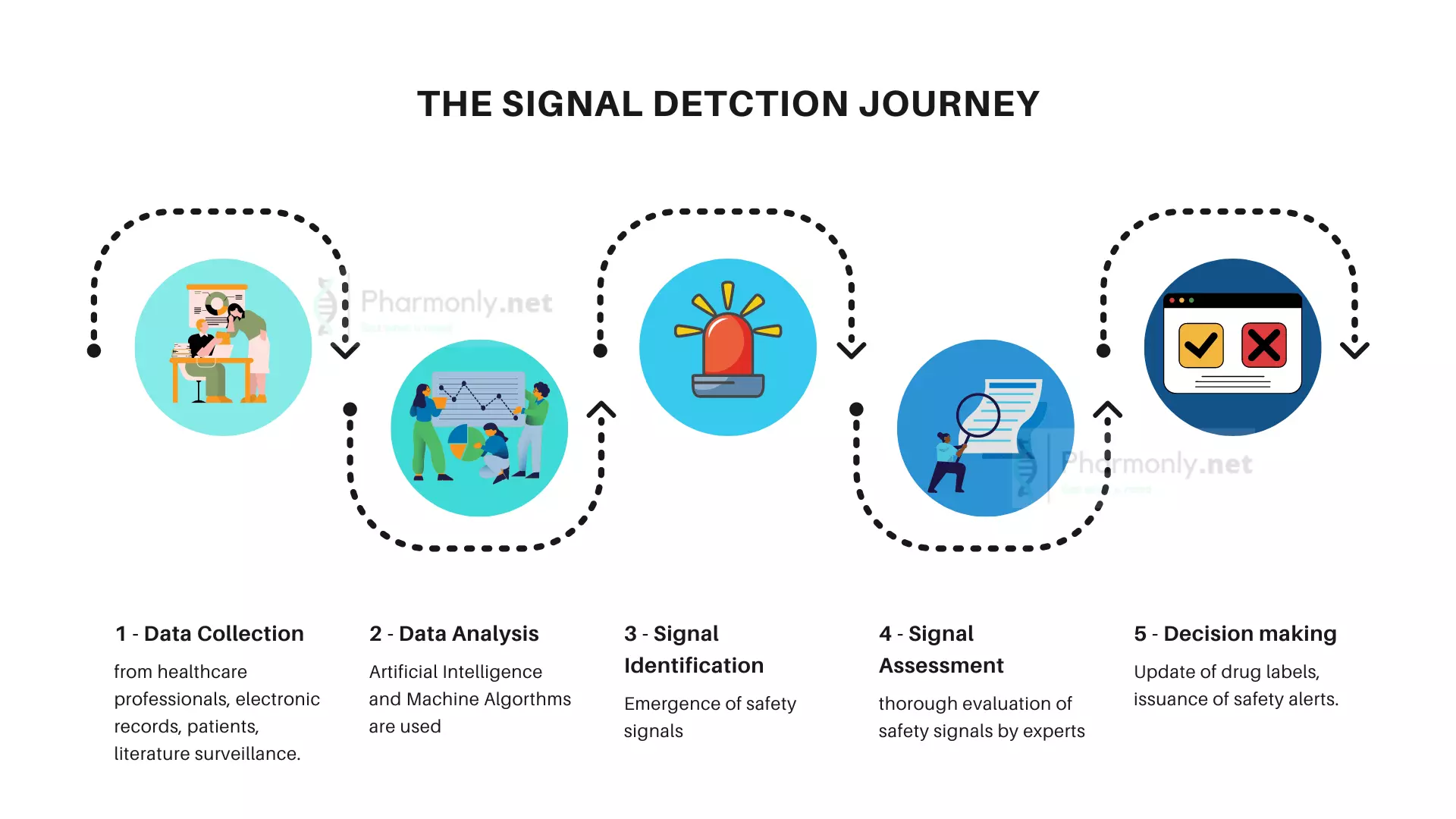
- Signal Detection: Detecting safety signals involves using statistical methods and data analysis to identify potential issues within the adverse event data. Once identified, signals are investigated further.
- Risk Assessment and Management: Assessing both known and potential risks associated with drugs is crucial. Strategies to minimize risks and plans for communicating risks are developed and implemented.
- Benefit-Risk Assessment: Continuously evaluating the balance between a drug’s benefits and risks is essential for regulatory decision-making. Adjustments to labeling and regulatory actions might be necessary.
- Safety Communication: Disseminating safety information to healthcare professionals, patients, and the public is done through clear and accurate labeling, advisories, and other communication channels.
- Quality Management: Ensuring quality involves implementing controls and assurance measures. Regular audits and inspections maintain compliance with pharmacovigilance standards.
- Training and Competence: Proper training ensures personnel involved in pharmacovigilance understand their roles and responsibilities, contributing to accurate and reliable safety assessments.
- Collaboration and Information Sharing: Collaboration among regulatory agencies, industry partners, and healthcare professionals facilitates sharing of safety information, best practices, and international harmonization efforts.
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: Ongoing monitoring of safety data detects emerging risks. Continuous improvement of pharmacovigilance processes based on lessons learned ensures effectiveness over time.
Challenges and Opportunities in Global Collaboration
The quest for global pharmacovigilance collaboration presents both challenges and opportunities as regulatory bodies, healthcare systems, and cultural nuances converge on the path to ensuring drug safety. Let’s navigate through these intricacies to understand the complexities of harmonizing efforts across borders.
Challenges: Navigating Differences
One of the foremost challenges lies in the disparities among regulatory requirements of various countries. Each nation follows its unique pharmacovigilance guidelines, reporting formats, and safety assessment processes. Bridging these differences can be intricate, requiring careful coordination to ensure a consistent approach to signal detection and risk assessment.
Cultural considerations also play a role in shaping pharmacovigilance practices. Differing perceptions of adverse events, healthcare practices, and patient engagement can impact reporting behaviors and signal identification. Overcoming these cultural barriers demands sensitivity and an understanding of how local contexts influence pharmacovigilance activities
Opportunities: Collaboration Beyond Boundaries
Amidst these challenges, global collaboration offers a wealth of opportunities to amplify drug safety efforts. Harmonizing reporting formats and procedures can lead to improved data exchange and streamlined practices. By creating a framework that accommodates regulatory diversity, international collaboration becomes a driving force behind a unified approach to pharmacovigilance.
Advancements in technology provide a gateway to data sharing and interoperability. Digital platforms enable real-time signal detection and assessment, fostering swift response to emerging safety concerns. Collaborative efforts in developing comprehensive pharmacovigilance databases can pool resources, creating a reservoir of safety data that transcends geographical limitations.
Towards a Unified Approach
The challenges and opportunities interweave, demonstrating the complexity of global pharmacovigilance collaboration. Regulatory bodies, healthcare professionals, and pharmaceutical companies must collectively address these challenges while embracing the opportunities that technology and shared resources offer.
In the grand tapestry of pharmacovigilance, global collaboration forms an essential thread. As international networks are strengthened, the potential for knowledge exchange, mutual learning, and collective action grows. Together, nations can surmount regulatory disparities, bridge cultural gaps, and ultimately enhance drug safety on a global scale.
In the upcoming sections, we will explore the initiatives that facilitate international collaboration, delving into the mechanisms that enable regulatory bodies to harmonize efforts, share data, and collectively respond to the ever-evolving landscape of drug safety.
International Collaboration Initiatives
The realm of pharmacovigilance recognizes no geographical boundaries. Through robust international collaborations and networks, the world unites to safeguard the health and well-being of individuals worldwide. Among these endeavors, the WHO Programme for International Drug Monitoring (PIDM) stands as a shining example of collective dedication to drug safety.
WHO Programme for International Drug Monitoring (PIDM)
The PIDM operates as a beacon of global pharmacovigilance cooperation. Established by the World Health Organization, PIDM fosters collaboration among more than 150 national pharmacovigilance centers worldwide. Through this network, countries share vital safety data, enabling a comprehensive assessment of adverse events and emerging signals.
Promoting Information Exchange
At the core of international collaboration lies the exchange of information. PIDM facilitates the sharing of safety data, allowing regulatory bodies and healthcare professionals to access insights from diverse healthcare settings. This information exchange transcends regional barriers, enabling a holistic understanding of drug safety profiles and emerging trends.
Capacity-Building for Self Practices
International collaboration goes beyond data exchange. PIDM and similar initiatives engage in capacity-building, equipping nations with the tools and knowledge to enhance pharmacovigilance practices. Workshops, training programs, and best practice dissemination empower regulatory bodies to adopt effective safety measures, regardless of their resource capacities.
Harmonizing Signal Detection
In a world of varied reporting systems and cultural nuances, signal detection can be complex. International collaboration initiatives help harmonize these efforts. When a signal emerges in one region, the collective network aids in evaluating its significance across borders. This united approach ensures timely responses to safety concerns.
The Power of Collective Action
The success of international collaboration initiatives lies in their ability to transform individual efforts into a global force for change. By unifying nations, these networks magnify the impact of pharmacovigilance, ensuring that drug safety transcends regional disparities and serves as a collective commitment to humanity’s well-being.
In the upcoming sections, we’ll explore the pivotal role of national pharmacovigilance centers in facilitating global collaboration. We’ll uncover how these centers serve as conduits for data exchange, mutual learning, and the cultivation of a safer healthcare environment on a global scale.
The Role of Pharmacovigilance Centers
Within the intricate tapestry of global pharmacovigilance collaboration, national pharmacovigilance centers emerge as vital nodes, connecting nations, and catalyzing the exchange of safety information. These centers play a multifaceted role in harmonizing efforts, fostering information sharing, and managing a global repository of drug safety data.
Facilitating Global Collaboration
National pharmacovigilance centers serve as conduits for international collaboration. They act as points of contact, facilitating communication among regulatory bodies, healthcare professionals, and pharmaceutical companies across borders. Through these centers, safety data flows seamlessly, transcending national boundaries to collectively build a comprehensive understanding of medication safety.
Enabling Safety Data Exchange
These centers establish the infrastructure for the exchange of safety data. By adhering to common reporting standards and data formats, they streamline the process of data sharing. This uniformity empowers regulatory bodies to swiftly identify emerging signals, assess risks, and collaborate in taking appropriate measures to protect public health.
Unifying Global Drug Safety Databases
In the quest for a safer healthcare environment, the collaboration between national pharmacovigilance centers extends to the management of global drug safety databases. These databases serve as reservoirs of safety information, allowing countries to draw insights from a vast pool of real-world data. The collaboration ensures that no corner of the world remains isolated from critical safety intelligence.
Strength in Numbers and Knowledge
The role of national pharmacovigilance centers extends beyond safeguarding their own nations; it encompasses a vision of shared responsibility for global health. These centers exemplify the ethos of international cooperation, transforming challenges into opportunities, and adversity into collective progress.
A Vision beyond Borders
The role of national pharmacovigilance centers extends beyond safeguarding their own nations; it encompasses a vision of shared responsibility for global health. These centers exemplify the ethos of international cooperation, transforming challenges into opportunities, and adversity into collective progress.
Transforming Patient Safety Through Global Collaboration
In the dynamic landscape of pharmacovigilance, global collaboration stands as a beacon of progress, illuminating the path to improved patient safety. By uniting regulatory bodies, healthcare professionals, and pharmaceutical entities across borders, this collective effort ensures the early detection of potential safety signals and facilitates swift safety actions. This unity has tangible real-world impacts, exemplified by instances where collaborative endeavors preempted adverse events and enhanced patient outcomes.
As nations pool their knowledge and resources, they empower informed decision-making, bolster public health, and build a foundation for a safer medical future. This chapter of global collaboration holds the promise of a world where medications heal without harm, a testament to the power of shared commitment in safeguarding human health.
Conclusion and Future Remarks: Pioneering a Safer Tomorrow
As we bid adieu to this exploration of pharmacovigilance’s global dynamics, we embrace the exhilarating potential that lies on the horizon. The journey through collaborative efforts, regulatory frameworks, and international networks has revealed a tapestry woven with commitment to patient safety. The road ahead shines bright with promise.
The future of pharmacovigilance paints a picture where cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence and data analytics will become indispensable allies. These tools will refine signal detection, elevate risk assessment, and expedite safety actions, driving us toward an era of more proactive and precise interventions.
Yet, the core remains unchanged: our shared dedication to public health. Through global collaborations and united endeavors, we’ll continue to evolve the pharmacovigilance landscape, transcending boundaries and nurturing a culture of patient safety. The strides we take today are the foundation of a healthier tomorrow, where medications heal, and safety prevails.
As we close this chapter, let’s carry forward the spirit of unity and vigilance. By engaging, reporting, and participating, each of us contributes to the mosaic of global pharmacovigilance. Together, we forge a world where medications are not just treatments but assurances of well-being. The journey continues, the vision endures, and we’re all part of the story—pioneers of a safer, healthier world.
Empower your Voice for Safer Medicines
Your voice matters, and your participation can shape the future of drug safety. Share your thoughts, experiences, and insights in the comments section below. Let’s create a space for open dialogue and mutual learning as we navigate the complex landscape of pharmacovigilance.
Stay connected with us by subscribing to our newsletter. Receive timely updates on the latest advancements, regulatory changes, and international collaborations in the world of pharmaceuticals. Together, we can foster a community dedicated to ensuring that medications remain a beacon of healing and wellness.
Pharmacovigilance Data Management and Reporting: Unveiling Safety Insights
Continue reading series.

Pingback: Pharmacovigilance Data Management and Reporting - Explained
Pingback: Future of Pharmacovigilance - Advancements in Drug Safety